Endocrine Therapy Provides TwentyYear Benefit in ER+ Breast Cancer
Integrative and Individualized cancer care is the best cancer care and yields the best long term outcomes. Making individualized care decisions and including a health model, not just a disease model and following the OutSmart Cancer® Diet Guidelines are core principles of the OutSmart Cancer® System.
Two years of adjuvant endocrine therapy in premenopausal patients with estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer can reduce the risk of recurrence at 20 years, according to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. (2) This study is meaningful because many oncologists recommend five to ten years of endocrine therapy. This study clearly demonstrates that only two years is sufficient to significantly reduce risk of breast cancer recurrence 20 years after completion of conventional oncology treatment. This study also demonstrates that women who are candidates for and who do not receive endocrine therapy have worse outcomes.
Furthermore this study demonstrates that women with low genomic risk should receive tamoxifen and women with high genomic risk should receive goserilin for best long term outcomes.
By including an integrative approach utilizing the health principles of the OutSmart Cancer® System, we can further manage the side effects of these treatments and support healthy function and quality of life for these women.
OUTSMART CANCER SYSTEM® Integrative Approach and Health Focussed Model
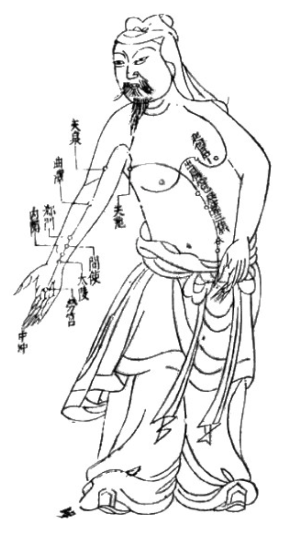 Especially supportive to management of adverse menopausal effects of endocrine therapy include acupuncture therapy(3), copper free bone mineral formula and optimized Vitamin D as well as traditional Chinese Herbal Tonics
Especially supportive to management of adverse menopausal effects of endocrine therapy include acupuncture therapy(3), copper free bone mineral formula and optimized Vitamin D as well as traditional Chinese Herbal Tonics
that nourish yin and blood and support kidney qi to modulate menopausal symptoms without estrogenic effects such as Er Xian Tang (Two Immortals Formula) and also formulas to address hormone depletion related mood dysregulation, depression and irritability such as Shu Gan Tang (Buplerum and Evodia Combination) to harmonize the liver qi and relieve stagnation of blood and emotions. Furthermore, patients with estrogenic cancers should be given guidance on restricting estrogenic foods from their diets as part of a lifelong plan to prevent recurrence. For example, both red meat (7) and alcohol (6) are known carcinogens linked to promotion of breast cancer and should be restricted. Following the OutSmart Cancer® Diet Guidelines is recommended
Monitoring for complications of endocrine therapies
Patients receiving Tamoxifen therapy (an oral selective estrogen receptor modifier) should have semi-annual uterine ultrasound to measure endometrial thickness to assess risk of uterine hyperplasia and neoplasm as a risk of tamoxifen therapy.
Patient receiving goserilin (an injectabl luteinizing hormone releasing hormone antagonist administered subcutaneously either every month or every 3 months) should monitor bone density by having a baseline DEXA bone density scan at inception and at 2 years and also Urine N-Telopeptide assay to monitor rate of loss of bone minerals due to medical menopause and estrogen blockade.
Results of Study
Researchers observed significant improvements in long-term distant recurrence-free interval (DRFI) for patients who received goserelin alone, tamoxifen alone, or the combination of goserelin and tamoxifen, when compared with patients who did not receive endocrine therapy.
However, combination goserelin and tamoxifen did not improve DRFI when compared with either agent alone.
Researchers assessed the 20-year benefit of endocrine therapy by analyzing data from the Stockholm trial (1990-1997). The analysis included 584 patients with ER+ breast cancer. The median age at baseline was 47 (range, 26-55) years, 91% of patients had progesterone receptor-positive tumors, and 88% had HER2-negative tumors.
Patients were randomly assigned to 2 years of goserelin (n=155), tamoxifen (n=135), combined goserelin and tamoxifen (n=149), or no adjuvant endocrine therapy (n=145).
In a multivariable analysis, any endocrine therapy was associated with a significant improvement in long-term DRFI, when compared with no endocrine therapy.
There was a significant improvement in DRFI with goserelin alone (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.32-0.75), tamoxifen alone (HR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.38-0.87), and goserelin plus tamoxifen (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.42-0.94).
However, there was no significant long-term benefit from the combination of goserelin plus tamoxifen, when compared with either agent alone. There was a significant interaction between goserelin and tamoxifen (P =.016).
The researchers also assessed the long-term benefit of endocrine therapy in patients with low genomic risk (n=305) and those with high genomic risk (n=158).
Patients with low-risk genomics had a significant improvement in DRFI with tamoxifen (HR, 0.24; 95% CI, 0.10-0.60), and patients with high-risk genomics had a significant improvement in DRFI with goserelin (HR, 0.24; 95% CI, 0.10-0.54).
Patients with high-risk genomics had significantly worse DRFI when tamoxifen was added to goserelin (HR, 3.36; 95% CI, 1.39-8.07). The interaction between goserelin and tamoxifen was significant in high-risk patients (P =.006) but not in low-risk patients (P =.080).
“This study demonstrates long-term benefit from 2 years of adjuvant endocrine therapy in ER-positive premenopausal patients,” the researchers concluded. “Furthermore, it suggests long-lasting benefit from tamoxifen in genomic low-risk patients with long-term risk of distant recurrence, whereas genomic high-risk patients have early risk and benefit from goserelin.”
Isoflavones genistein and daidizen are phytochemicals derived from soy act that act as MILD selective estrogen receptor modulators. These isoflavones need to be taken in very high doses on a long term basis to achieve a clinical impact and are mild in comparison to pharmaceuticals. A recommended daily dose of genistein is 1000mg 3x/day
This study will help us support patients in making educated and informed choices and in making sure that their oncologists are practicing in accordance with the most current research and guidelines and that patients





