Lifestyle Factors That Impact Breast Cancer Risk
- Alcohol: Drinking Alcohol Increases Risk of Breast Cancer
- Weight and Body Composition: Excess body fat increases risk for post-menopausal breast cancer. Lean muscle, low body fat decreases risk of pre-menopausal breast cancers
- Physical Activity: Sedentary behavior is linked to increased risk of breast cancer, while being active decreases the risk of breast cancer
Vigorous activity decreases the risk for pre-menopausal breast cancer.
Moderate activity decreases risk for post-menopausal breast cancer.
Some evidence indicates that people who are physically active (both before and after diagnosis) have a greater chance of surviving breast cancer.
- Breastfeeding: Reduces risk of both pre- and post-menopausal breast cancer
- Sleep: Women who report sleeping less than 5 hours per night before diagnosis have an increased risk of dying from breast cancer compared to women whose pre-diagnosis sleep pattern was 7-8 hours per night. Women who have disrupted circadian rhythms due to night shift work have an increased risk of breast cancer.
Does Stress Cause Cancer?
Maladaptive and ongoing responses to stress mediated by the Autonomic Nervous System and Hypothalamic Pituitary Axis promote a tumor microenvironment that favors inflammation, oxidative stress, poor glycemic control, carcinogenesis, proliferation, angiogenesis and metastasis
Physiological Pathways, Bio-behavioural Processes and Oncogenesis:
- Environmental and social processes activate interpretive processes in the central nervous system (CNS) that can subsequently trigger fight-or-flight stress responses in the autonomic nervous system (ANS) or defeat/withdrawal responses through the activation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA)
- Individual differences in perception and evaluation of external events (coping) creates variability in individual ANS and HPA activity levels.
- Over long periods of time, these neuroendocrine dynamics can alter various physiological processes involved in tumorigenesis, including oxidative metabolism, DNA repair, oncogene expression by viruses and somatic cells, and production of growth factors and other regulators of cell growth.
- Once a tumour is initiated, neuroendocrine factors can also regulate the activity of proteases, angiogenic factors, chemokines and adhesion molecules involved in invasion, metastasis and other aspects of tumour progression.
- CNS processes can also shape behavioural processes that govern cancer risk (for example, smoking, transmission of oncogenic viruses or exposure to genotoxic compounds).
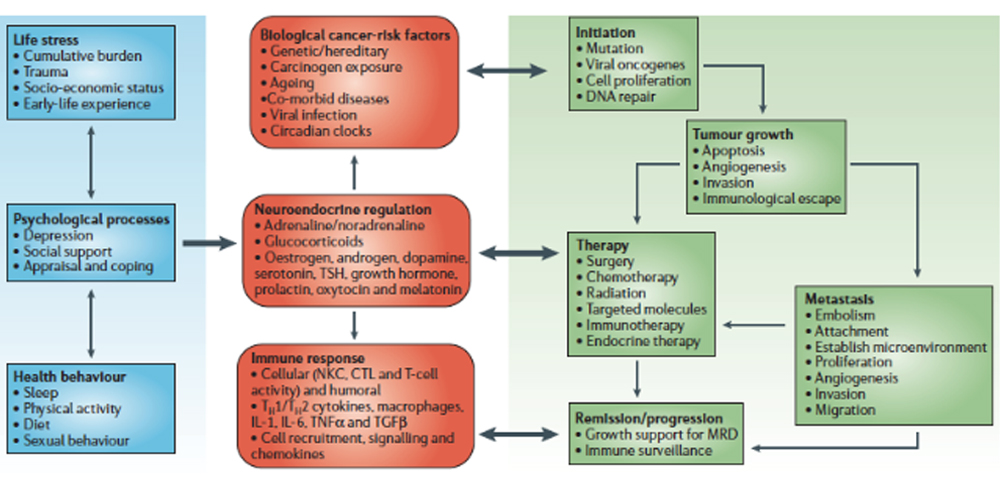
Integrated Model of Bio-behavioral Influences on Cancer Pathogenesis Through Neuro-Endocrine Pathways
In this model, bio-behavioural factors such as life stress, psychological processes and health behaviours (blue panel) influence tumour-related processes (green panel) through the neuroendocrine regulation of hormones, including adrenaline, noradrenaline and glucocorticoids (red panel).
Central control of peripheral endocrine function also allows social, environmental and behavioural processes to interact with biological risk factors such as genetic background, carcinogens and viral infections to systemically modulate malignant potential (red panel).
Direct pathways of influence include effects of catecholamines and glucocorticoids on tumour-cell expression of genes that control cell proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, metastasis and immune evasion (green panel).
Stress-responsive neuroendocrine mediators can also influence malignant potential indirectly through their effects on oncogenic viruses and the cellular immune system (red panel).
These pleiotropic hormonal influences induce a mutually reinforcing system of cellular signals that collectively support the initiation and progression of malignant cell growth (green panel).
Furthermore, neuroendocrine deregulation can influence the response to conventional therapies such as surgery, chemotherapy and immunotherapy (green panel).
In addition to explaining bio-behavioural risk factors for cancer, this model suggests novel targets for pharmacological or behavioural intervention.
(CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocytes; IL, interleukin; MRD, minimal residual disease; NKC, natural killer cell; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β; TNFα, tumour-necrosis factor-α; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone.)
Dr. Nalini’s Adrenal Stress-Immune Support Protocol
DAYTIME
Designs for Health Adrenotone 2/3x/day. With meals
All-in-one synergistic adrenal support formula.
Metagenics Immucore 1/3x/day. With meals
Multidimensional Support for Healthy Immune Function
BEDTIME
Integrative Therapeutics Cortisol Manager 2 caps one hour before bedtime
- Safe for use every night
- Stress reducing sleep aid
- Reduces cortisol levels for stress reduction and restful sleep.
https://us.fullscript.com/protocols/chilkov-dr-nalin-s-adrenal-stress-immune-support-kit
Treatment Plan should include
Patient Teaching, Lifestyle and Dietary Guidelines and ongoing behavior change support
- Dietary Guidelines -Nutrient Repletion-Glycemic Control
- How to nurture parasympathetic tone
- Sleep Hygeine
- Self Regulation-Resilience- Stress and Mood Management guidelines
- Monitoring Heart Rate Variability
- Encourage Meditation-Tai Chi-Yoga-Deep Relaxation, Time in Nature
- Acupuncture
- Massage
- Importance of Social Support